AI-based Volunteer Engagement for Crowdsourcing Food Rescue Platforms (Predicting and Presenting Task Difficulty for Crowdsourcing Food Rescue Platforms)
Food rescue platforms rely on volunteers to deliver food to low-resource communities to fight food insecurity, but volunteer engagement is a main challenge in operations. This research looks to address the “right” demographic of volunteers to recruit, how to effectively engage them, and when to do so.
Research Methodology
A hybrid model with tabular and natural language data was used to predict the difficulty of a given food rescue trip. Focus group sessions with 10 volunteers and staff members were conducted where 6 different scaffolding methods present the ML model to users. Stakeholder interviews were also conducted to understand their perspectives on how to integrate such predictions into volunteers’ workflow.
Research Goals
This research aims to better understand how to improve volunteer engagement and retention through crowdsourcing volunteering platforms and predict how easy/hard a task will be for a volunteer.
Research Outcomes
Three LLM-based methods (natural language explanations, tag-based explanations, and augmented tag-based explanations) generated explanations for ML predictions. These results are currently being adopted with Food Rescue Hero to run a randomized controlled trial of the volunteer engagement algorithms.
Sponsors or Additional Collaborators
Food Rescue Hero
Carnegie Mellon University
University of Illinois
Slide Text
- AI-based Volunteer Engagement for Crowdsourcing Food Rescue Platforms
-
AI-based Volunteer Engagement for Crowdsourcing Food Rescue Platforms
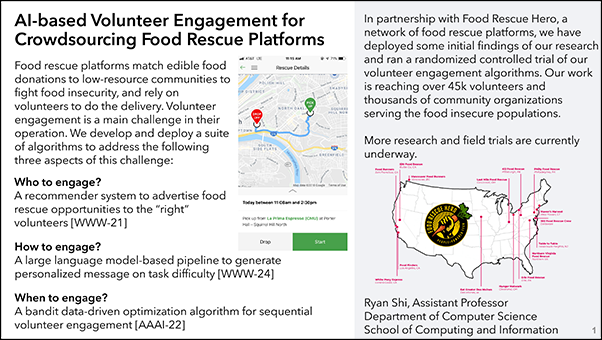
Food rescue platforms match edible food donations to low-resource communities to fight food insecurity, and rely on volunteers to do the delivery. Volunteer engagement is a main challenge in their operation. We develop and deploy a suite of algorithms to address the following three aspects of this challenge:
Who to engage?
A recommender system to advertise food rescue opportunities to the “right” volunteers [WWW-21]How to engage?
A large language model-based pipeline to generate personalized message on task difficulty [WWW-24]When to engage?
A bandit data-driven optimization algorithm for sequential volunteer engagement [AAAI-22]In partnership with Food Rescue Hero, a network of food rescue platforms, we have deployed some initial findings of our research and ran a randomized controlled trial of our volunteer engagement algorithms. Our work is reaching over 45k volunteers and thousands of community organizations serving the food insecure populations.
More research and field trials are currently underway.
A map graphic shows locations of food rescue organizations across the country, including 412 Food Rescue in Pittsburgh; Erie Food Rescue in Erie, PA; and Hunger Network in Cleveland.
Ryan Shi, Assistant Professor
Department of Computer Science
School of Computing and Information
